Working with USB webcams on your Raspberry Pi
In most cases it is best to use a Raspberry Pi camera module. However, to help you with those cases you still want to use a USB webcam, follow the below guide.
Table of contents
- Pros and cons of a USB webcam
- Setting up and using a USB webcam
- Controlling the webcam with Python
- Setting up multiple USB webcams
Pros and cons of a USB webcam
USB Webcams generally have inferior quality to the camera modules that connect to the CSI interface. They can also not be controlled using the raspistill and rasivid commands in the terminal neither by the picamera recording package in Python. Nevertheless, there may be reasons why you want to connect a USB camera to your Raspberry Pi, such as because of the benefit that it is much easier to set up multiple camera’s with a single Raspberry Pi (see below).
Setting up and using a USB webcam
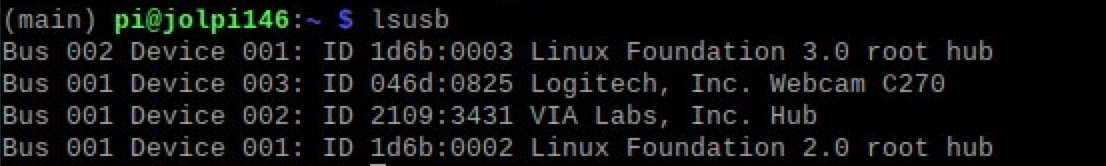
You can control a USB webcam both using bash in the terminal and with Python. First plugin the camera and see if the Raspberry Pi recognises it by entering lsusb in the terminal. It should show something like this:
To command the camera in the terminal I suggest to use the fswebcam package. To install:
sudo apt install fswebcam
To take an image with a certain resolution and hide the standard banner:
fswebcam -r 1280x720 --no-banner /images/image1.jpg
To find the supported webcam resolutions:
v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext
You could also use ffmpeg to take images and video. To install:
sudo apt install ffmpeg
To take an image:
ffmpeg -f v4l2 -video_size 1280x720 -i /dev/video0 -frames 1 out.jpg
A more advanced alternative is mjpeg-streamer, which enables you to stream the camera in a browser. You can find a detailed tutorial how to set that up here.
Controlling the webcam with Python
A number of solutions exist to connect to the USB camera with Python. Unfortunately the picamera software does not work with USB webcams. I suggest to use OpenCV. To help install OpenCV, follow my guide here. Now to record a single image:
import cv2
cam = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
ret, image = cam.read()
cv2.imshow('Imagetest',image)
k = cv2.waitKey(1)
if k != -1:
break
cv2.imwrite('/home/pi/testimage.jpg', image)
cam.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
There are many other options available with opencv. I suggest to read the documentation at opencv.org.
Setting up multiple USB webcams
You can connect as many webcams as you want as long as they are powered up per their requirements, such as using a powered USB hub. Each usb web cam that you connect gets listed under /dev/video<n> where n, starting at 0 for camera 1, is the id of the device.
To list your devices:
ls /dev/
You can set the device to use for recordings with the fswebcam software with the --device flag. For example, to take an image with the second connected USB webcam using fswebcam:
fswebcam --device /dev/video1 image.jpg
And with Python and OpenCV you can just set cv2.VideoCapture to 1.